When I first stumbled across Matt J. Vollum’s article, The Potential for Social Media Use in K-12 Physical and Health Education, my initial reaction was that this was another case of using social media just for the sake of it. However, the more I read about social media use in health and physical education the more benefits I see.
For the purpose of this blog post, I would like to use Wikipedia’s definition of social media. “Social media is the social interaction among people in which they create, share or exchange information and ideas in virtual communities and networks.”
Switching gears slightly while remaining on the topic of social media, my wife gave birth to our first child in February. Since then, she developed a network of new mothers with children around the same age as our daughter. Several of the group members have already talked about a second child but felt like they wanted to increase their core strength before putting their bodies through the stress of another pregnancy. One way they came up with to prepare for this was to start to run together, but that wasn’t always feasible because of schedules. Instead, they decided to utilize social media. Each group member downloaded the same smartphone app, Couch-to-5k, by Active Network. The app allowed them to track their individual progress, be each others cheerleaders, and allowed them to send each other motivational messages of support. They also found the benefits of collectively sharing technical running knowledge. If adults enjoy motivationally driven collaborate exercise, then why not kids?
Vollum discusses the potential of social media use in health and physical education by discovering how health and wellness programs outside of education are currently using social media. He also uses existing research on the topic of social media, which exists in general education. His argument is simple. If the use of social media in healthy living is useful outside of education and is already being used in other areas of education then perhaps, it might be beneficial to include in health living curriculums in schools.
According to a recent Media Smarts article titled, Young Canadians In A Wired World, 99% of students surveyed from grades 4-11 had access to the Internet outside of school. 81% of those students also used social media that included but was not limited to Facebook, Twitter, and Google+ (Steeves, 2014)
Vollum’s research looked at three areas of social media and education:
- The relationship between social interaction and the educational experience.
- Vollum found that social media has the potential to increase social presence, a feeling of connectedness towards others, which can lead to brighter educational experience and greater accomplishment (Vollum, 2014)
- The relationship between social media and social interaction.
- Vollum found that when information can be personalized it becomes more meaningful to the learner, and social media can increase the sense of belonging and connectedness with a prolonged membership on social media (Greenhow, 2011)
- The relationship between social media and community and personal physical and health education outside of the K-12 setting.
- Social media has the opportunity to develop relationships and partnerships in health and behavior changes thus increasing the communication, which can lead to increasing levels of education (Hanson et al., 2011)
- Students in today’s world are already using social media in their educational setting. If increased social presence improves education and a large percentage of students are discussing education already then it would seem reasonable to say that social media use in a K-12 physical/health education environment can increase the educational experience and/or achievement (Vollum, 2014)
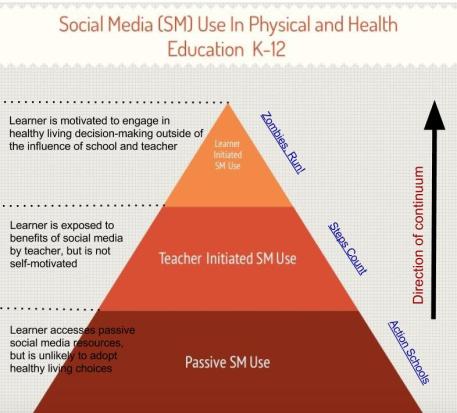
The Continuum of Social Media Use in Health and Physical Education
When one looks at current social media use in health and physical education, a clear hierarchy of practical use is visible. At the base level, organizations that promote healthy living and physical education in partnership with schools have developed a passive form of interaction to deliver their message. Healthy living champions typically utilize a webpage, or social media spaces such as Twitter, YouTube, Google+, or Facebook. Users with an interest in healthy living visit the site to review documents and multimedia resources. An example of this is the Action Schools BC website, which may be referred to as passive social media use.
When K-12 schools move away from passive social media use to enhance healthy living they take a step closer toward using social media to its full potential. Teacher-centered social media use is the next logical step in the continuum towards Learner-centered social media use. In this stage, teachers use social media to create profiles and logs for students to record data about their healthy living experiences. An example of this is Steps Count, which provides a platform for teachers to set up a class to track and chart student’s step counts using pedometers.
Schools may say they use social media to its full potential, when learners work collaboratively outside of the classroom and without direct influence from their teachers to develop independent, healthy living habits. An example of this is Zombies, Run! which has amassed over 800 000 members worldwide. Players combine social media with physical activity.
In contrast to the clear benefits of Zombies, Run! Meyer, in his Handbook of Multimedia Learning, disagrees with the use of multimedia agents of learning. In our case, Mayer would say that the feedback delivered by the narrator and zombie in the running app may not lead to increased motivation and learning. Meyer states, Well designed studies find that when the effects of well designed instructional methods provided by the agent are separated from the effects of the presence of the agents, no learning benefits are found (Mayer, 2005). If I gave my learners the option of running around the school track, or running around the community while listening to a highly interactive adventure, I’m pretty sure which option they would take.
Benefits of Social Media Use In Physical and Health Education
There are many advantages of including social media use in K-12 healthy living curriculum. Coaches may use video to capture and analyze a performed skill before sharing it with members of a team to learn from. Younger students could use social media to track their eating habits and compare it with other children around the world. Teacher can use the power of social to add elements of gameplay into physical education, which may grab the attention of the sedentary video game generation.
References
Greenhow, C. (2011). Online social networks and learning. On the Horizon, 19(1), 4–12. doi:10.1108/10748121111107663
Hanson, C., West, J., Neiger, B., Thackeray, R., Barnes, M., & McIntyre, E. (2011). Use and Acceptance of Social Media Among Health Educators. American Journal of Health Education, 42(4), 197–204. doi:10.1080/19325037.2011.10599188
Mayer, R. E. (2005). The Cambridge handbook of multimedia learning. IThe Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning (Vol. 16, p. 663). doi:10.1075/idj.16.1.13pel
Steeves, V. (2014). Life Online.
Vollum, M. J. (2014). The potential for social media use in K-12 physical and health education. Computers in Human Behavior, 35, 560–564. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2014.02.035